I am a seasonal IT professional with a background on VMware, Storage, Backup, Unix, and Project liaison experience. I have held positions working on technologies like Netapp, EMC, IBM, Cohesity storage and Backup supporting SAN and NAS Environment. I have held roles of IT administrator, engineer, team lead and project liaison. This blog is for Storage and Backup Professionals, and content are derived from vendor as well as my own experience.
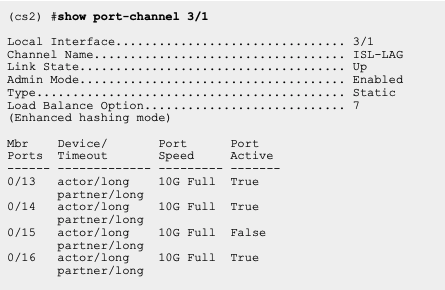
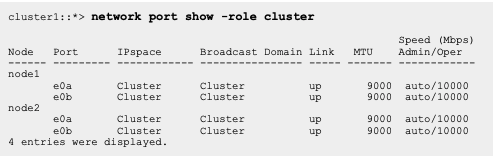
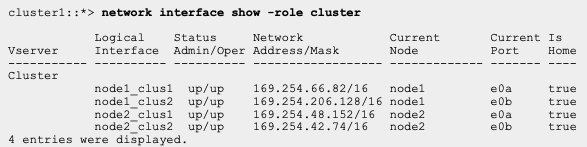
............................................................................................................................................................................Helpful display/Show commands on Cisco SAN Platform.
show zone
Displays zone information for all VSANs.
show zone vsan 1
Displays zone information for a specific VSAN.
show zoneset vsan 1
Displays information for the configured zone set.
show zoneset vsan 2-3
Displays configured zone set information for a range of VSANs.
show zone name Zone1
Displays members of a zone.
show fcalias vsan 1
Displays fcalias configuration.
show zone member pwwn 21:00:00:20:37:9c:48:e5
Displays membership status.
show zone statistics
Displays zone statistics.
show zone statistics read-only-zoning
Displays read-only zoning statistics.
show zoneset active
Displays active zone sets.
show zoneset brief
Displays brief descriptions of zone sets.
show zone active
Displays active zones.
show zone status
Displays zone status.
show zone
Displays zone statistics.
show running
Displays the interface-based zones.
Here is a depiction of SAN Zoning.
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/i/000001-100000/75001-80000/79001-80000/79537.ps/_jcr_content/renditions/79537.jpg
##How to delete device-alias name from current zone/zoneset
#config t
#dev data
#no dev-alias name hostname_portA
#dev-alias commit
#exit
##How to confirm if specific wwpn is currently logged in to fabric
#show flogi | include xx:xx:xx:xx
## How to list all fabric logins on switch
#show flogi database
##Show all configuration
#show running-conifg
##Reboot individual Port
#config t
#int fc3/1
#shut
#noshut
#int fc3/1
#show int fc3/1
##Display all port details
#show interface brief
You are Welcome :)
Source: www.cisco.com